ADAS Overview
ADAS Overview in Corby
Book at Central Autopoint
Get an instant price that you can book for free 24/7 and don’t pay until the day
Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is a system used to help avoid accidents by always keeping your car a safe distance from the traffic ahead.
Top tip: Adaptive Cruise Control uses a radar-based system that does not usually require calibration. However, some systems use cameras to see objects and will require a calibration after fitting a replacement windscreen.
Adaptive Headlights
Adaptive headlights are designed to make driving in low-light conditions safer by increasing the visibility around curves and over hills. This advanced feature uses steering input to make sure that the vehicle’s path is always lit up .
Top tip: Adaptive Headlights use camera-based systems that will require calibration after a windscreen replacement.
Autonomous Emergency Braking
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) is a feature that helps improve safety by identifying critical situations early and warning the driver. AEB also can reduce the chance of an accident by lowering the speed before collision.
Top tip: AEB systems use both lidar and radar technology. However, some systems do use cameras to detect objects and will require a calibration after fitting a new windscreen.
Blind Spot Awareness
This feature alerts you when another vehicle or object is in your blind spot. Extremely useful when changing lane, Blind Spot Awareness can help prevent collisions.
Top tip: This ADAS system uses radar technology that will not require calibration after a windshield replacement.
Lane Departure Warning
This advanced system uses cameras to detect if the driver is unintentionally straying out of its lane. It alerts the driver with an audible warning or a vibration on the steering wheel.
Top tip: Lane Departure Warning uses camera-based technology that will require calibration if you replace your windscreen.
Traffic Sign Recognition
Using a front-facing camera, this ADAS system detects traffic signs. Once this happens, it is then relayed onto the dashboard to alert the driver.
Top tip: This advanced system uses cameras to detect traffic signs and will require a calibration if you replace your windshield.
ADAS calibration checklist
Remove any additional loading
For us to carry out a successful ADAS calibration, we need to make sure that your vehicle has no additional loading. This includes fixed loading such as external racking, roof racks and canopies.
However, some commercial vehicles will have permanent fixtures, which will have to stay on the vehicle for us to carry out a successful windscreen calibration.
Full Tank of Fuel
Some vehicles will need to have a full tank of fuel when carrying out a camera calibration. This is to help make sure that the sensors are calibrated accurately and to the manufacturer’s required standard.
Some of the vehicle makes and models include:
- Honda
- Nissan Qashqai
- Nissan X-Trail
- Toyota Avensis (2016/2017)
- Toyota Auris (2016/2017)
- Toyota Verso
Full size wheels
For us to perform a successful ADAS calibration, we will need your vehicle to be fitted with 4 full-sized wheels. Each wheel will need to have their tyre pressures in line with the manufacturer's specification.
More information regarding tyre pressures can usually be found in your vehicle handbook.
FAQ
What is ADAS calibration?
An ADAS calibration is a process carried out to correctly align the cameras and sensors of a car so that its ADAS system can work as intended.
Why do I need a windscreen calibration?
Most ADAS features rely on a group of cameras or sensors to do their job. They usually sit inside a car windscreen and when a glass replacement is carried out, its angle and position changes.
A calibration is performed to correct this, so that your vehicle's ADAS is working as intended.
If a calibration is missed out, an ADAS feature may not work like it should and could cause a potential risk to you and others on the road.
What’s the difference between dynamic and static calibration?
Dynamic calibration involves driving the vehicle to complete the process.
Static calibration takes place at our site. Here, we use levelled flooring and specialist equipment to make sure that we can complete a successful calibration.
How long does calibration take?
This may differ dependant on the vehicle. We would allow between 1 – 2 hours.
When should I get ADAS calibration?
Glass replacements can cause small unexpected changes in the angle of a camera. This can be the difference between a car avoiding an accident or not.
That’s why your vehicle manufacturer strongly recommends getting an ADAS calibration with your replacement windscreen.
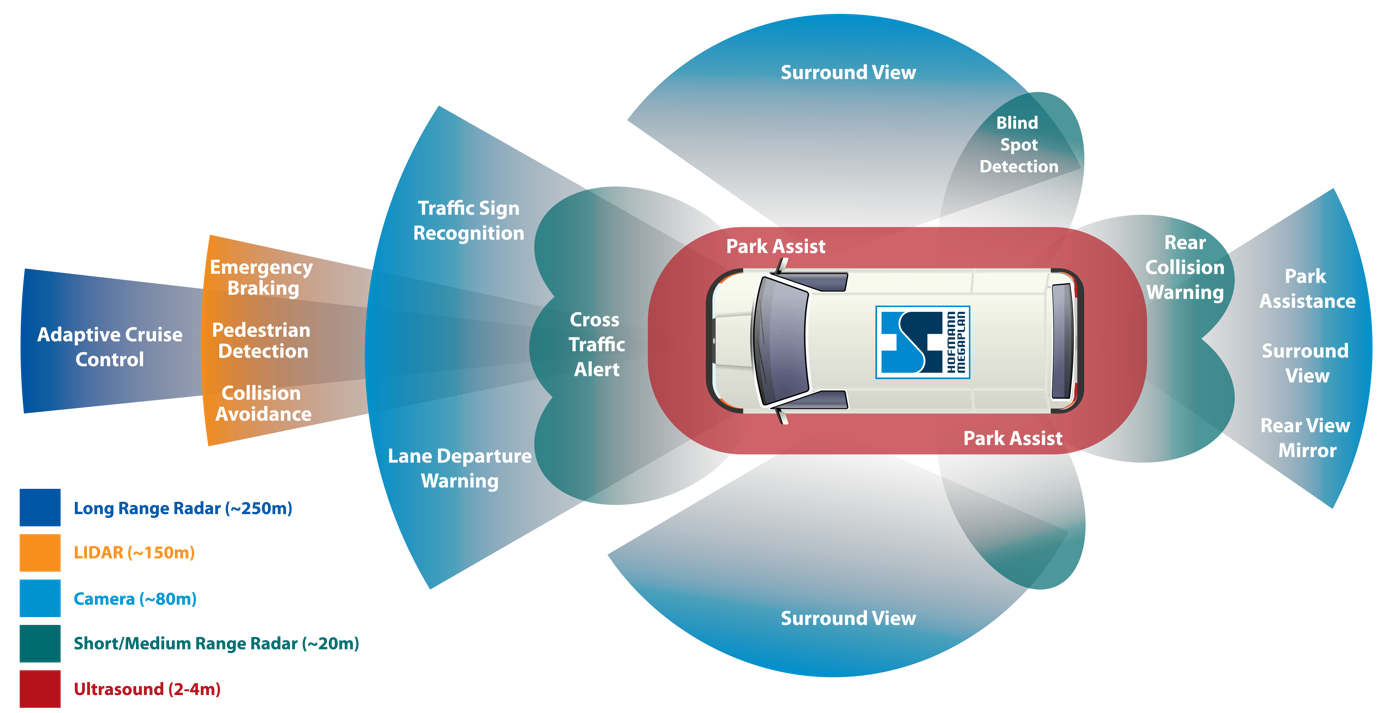
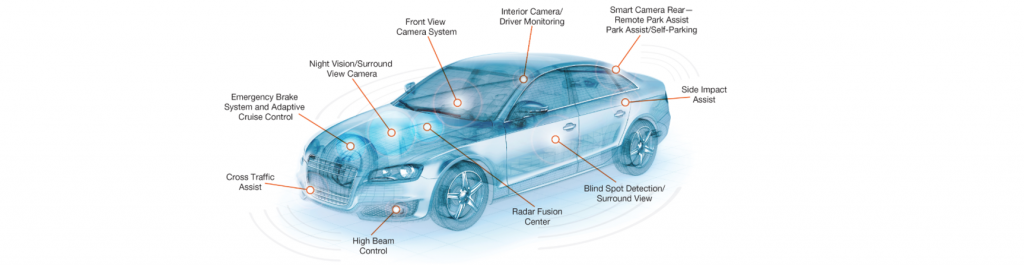
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) – Automatically adjusts the vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead.
Adaptive Light Control (ALC) – Swivelling curve lights (Cornering illumination). Increases visibility around curves and over hills in low-light conditions.
Anti-lock braking system (ABS) – Prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, to maintain traction with the road.
Automotive Night Vision – infrared sensors that use thermal imaging to help drivers see distance in poor sight conditions.
Blind Spot Monitor (BSM) – Sensors that provide visual, audible, or tactile warning of obstructions located in the vehicle’s blind spot.
Crosswind Stabilisation – Sensors to detect forces and apply brakes as necessary to counteract strong winds.
Cross Traffic Assist – Detects objects that may not be visible to drivers.
Driver Monitoring System (DMS) – Also known as driver drowsiness detection. Sensors which can track eye movements and reaction times in drivers to alert the driver when their attentiveness slips.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) – A system which detects and implements safeguards to reduce loss of traction.
Emergency Brake Assistant (EBA) – Analyses the speed and force with which the brake is applied, and if an emergency brake is detected, the system takes control to complete the emergency brake.
Euro NCAP – The European New Car Assessment Programme, a safety performance assessment programme.
Glare-free high beam and pixel light – Selective road lighting. A system which detects objects in front of and to the rear of the vehicle and selectively reduces the high beam to avoid glare for other road users.
Hill descent control – Uses ABS to control the vehicle’s speed when descending an incline.
Intersection assistant – Monitors traffic at junctions and warns the driver of hazardous situations.
Lane departure warning system (LDW) – Alerts the driver if the vehicle is straying from the road markings without indicating.
Lane keep assist – Senses road markings and takes control of the vehicle to remain within the lane.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) – A laser-based method of detection.
Park Assist – Automatic parking. Autonomous parking manoeuvres.
Parking sensors – Alerts the driver to obstacles while reversing.
Pre-Crash System – Forward collision warning and collision avoidance system. A system which detects and implements safeguards to reduce or avoid a potential crash.
Radio Detection and Ranging (RADAR) – A method of detection that sends out radio waves.
Rain sensor – Automatically applies the windscreen wipers if moisture is detected on the windscreen.
Recalibration – The process in which ADAS sensors and cameras are re-aligned.
Road sign recognition – Technology which uses image processing to detect speed limits.
Sensor fusion – The combined inputs of different sensors to process information more accurately.
Supplemental restrain system (SRS) – Safety systems within the vehicle, such as airbags, that work secondarily to the seat-belts.
Traction control system (TCS) – A secondary function of the electronic stability control.
Traffic sign recognition – Technology which uses image processing to detect traffic signs.
Turning assistant – A system which monitors oncoming traffic when turning against the direction of traffic.
TPMS – Tyre pressure monitoring system (TPMS) – A system which monitors tyre pressure to report to the driver.
